Child Brain Development
Childhood is a period of rapid growth and development, particularly in the brain. Understanding the stages of child brain development can help parents and caregivers support their child's learning and overall well-being. Here are the key stages of child brain development:
1. Prenatal Development
Brain development begins in the womb, even before birth. During the prenatal period, the basic structure of the brain is formed, including the neurons and neural pathways that will serve as the foundation for future learning and development. Factors such as maternal nutrition, exposure to toxins, and maternal stress can impact prenatal brain development.
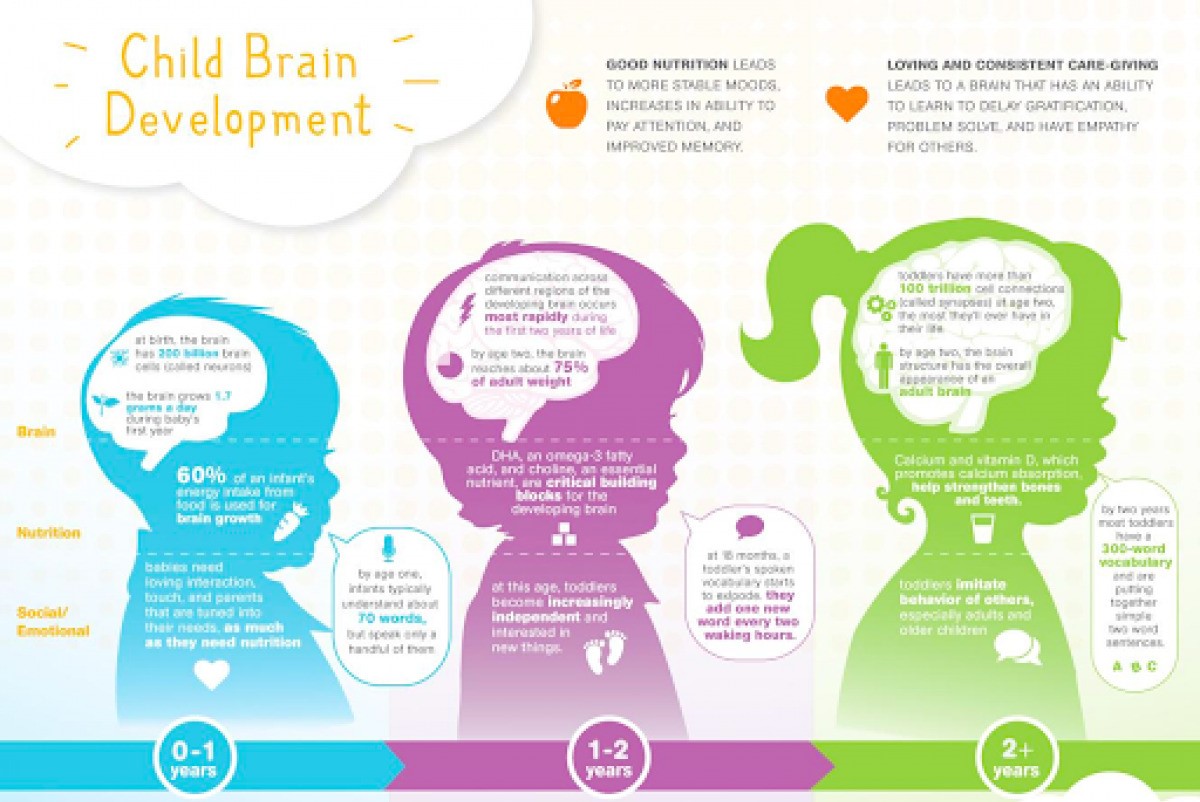
2. Infancy (0-2 years)
The first two years of life are characterized by rapid brain growth and development. During this period, the brain undergoes significant changes, including the formation of synapses, the connections between neurons. Infants begin to develop basic sensory and motor skills, such as vision, hearing, and grasping objects. The caregiver-child relationship plays a crucial role in shaping early brain development through responsive interactions and emotional bonding.
3. Early Childhood (2-6 years)
During early childhood, the brain continues to grow and refine its neural connections. This period is marked by rapid development in language skills, cognitive abilities, and social-emotional skills. Children begin to explore the world around them more actively, asking questions, solving problems, and developing a sense of autonomy. Play-based activities and interactive experiences are essential for stimulating brain development during this stage.
4. Middle Childhood (6-12 years)
In middle childhood, the brain becomes more specialized and efficient in processing information. Cognitive skills such as attention, memory, and logical reasoning continue to improve, allowing children to engage in more complex problem-solving tasks and academic learning. Social relationships become increasingly important, and children begin to develop a sense of identity and self-esteem.
5. Adolescence (12-18 years)
During adolescence, the brain undergoes significant changes in structure and function, particularly in areas responsible for higher-order thinking and emotional regulation. The prefrontal cortex, which is involved in decision-making and impulse control, continues to develop into early adulthood. Adolescents experience heightened emotions and may engage in risky behaviors as they navigate the transition to adulthood. Supportive relationships, healthy lifestyle habits, and opportunities for self-expression are crucial for promoting positive brain development during this stage.
6. Adulthood
While brain development is most rapid during childhood and adolescence, the brain continues to undergo changes throughout adulthood. Neural plasticity, the brain's ability to adapt and reorganize in response to experiences, remains present throughout life. Continued learning, social engagement, and cognitive stimulation are important for maintaining brain health and function in adulthood and beyond.
10 Tips to Develop Your Child's Intelligence
1. Encourage Curiosity
Curiosity is the spark that ignites the flame of intelligence. Encourage your child to ask questions, explore their surroundings, and seek answers. Foster their natural curiosity by providing opportunities for discovery and learning. Engage in conversations that stimulate their inquisitive nature and celebrate their thirst for knowledge.
2. Reading Together
Reading is a gateway to knowledge and imagination. Make reading a cherished part of your daily routine by reading to your child from an early age. Choose a variety of books that cater to their interests and curiosity. Encourage them to read independently as they grow older and celebrate their accomplishments along the way.
3. Promote Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a critical skill that underpins intelligence. Provide your child with puzzles, games, and challenges that require them to think critically and creatively. Encourage them to persevere in the face of obstacles and celebrate their successes. By fostering a problem-solving mindset, you equip your child with valuable tools for navigating the complexities of the world.
4. Provide a Stimulating Environment
Create an environment that sparks curiosity and encourages exploration. Surround your child with stimulating toys, books, and activities that engage their senses and imagination. Foster a love for learning by exposing them to diverse experiences and opportunities for discovery. Encourage them to explore their interests and pursue their passions.
5. Foster Creativity
Creativity is the hallmark of intelligence. Encourage your child to express themselves creatively through art, music, storytelling, and imaginative play. Provide them with the freedom to experiment, make mistakes, and learn from their experiences. Celebrate their unique talents and encourage them to think outside the box.

6. Support Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is as important as cognitive intelligence. Help your child develop empathy, self-awareness, and effective communication skills. Teach them to recognize and regulate their emotions, as well as understand the feelings of others. Foster meaningful connections and teach them the value of kindness, compassion, and empathy.
7. Encourage Physical Activity
Physical activity is essential for both physical and mental well-being. Encourage your child to engage in regular physical activity, whether it's playing outside, participating in sports, or simply going for a walk. Physical exercise not only improves cognitive function but also enhances mood, concentration, and overall brain health.
8. Limit Screen Time
Excessive screen time can impede intelligence development. Set limits on screen time and encourage alternative activities that promote active engagement and interaction with the real world. Encourage your child to explore their interests offline, engage in creative pursuits, and spend quality time with family and friends.
9. Provide a Positive Learning Environment
Create a supportive and encouraging atmosphere at home where learning is celebrated and mistakes are seen as opportunities for growth. Be actively involved in your child's education, providing guidance, encouragement, and support every step of the way. Foster a love for learning that extends beyond the classroom and into all aspects of life.
10. Be a Role Model
Lead by example and demonstrate the traits you wish to instill in your child. Model curiosity, resilience, creativity, and empathy in your own actions and interactions. Show them that intelligence is not just about knowledge but also about character, integrity, and compassion. Be a source of inspiration and encouragement as they embark on their journey of discovery and growth.
Conclusion
Developing your child's intelligence is a multifaceted endeavor that requires patience, dedication, and a holistic approach. By nurturing their curiosity, fostering their creativity, and supporting their emotional and physical well-being, you lay the foundation for a lifetime of learning and growth. Remember that intelligence is not solely determined by genetics but also by the environment and opportunities you provide. Embrace each day as an opportunity to inspire and empower your child to reach their full potential.
FAQs
1. How can I encourage my child to read more?
- Set aside dedicated time for reading each day and make it a fun and enjoyable activity.
2. What are some ways to promote problem-solving skills in my child?
- Provide puzzles, games, and challenges that require critical thinking and creative problem-solving.
3. How much screen time is appropriate for my child?
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends limiting screen time to no more than 1-2 hours per day for children ages 2-5.
4. How can I foster creativity in my child?
- Encourage open-ended play, provide art supplies, and expose them to a variety of creative outlets such as music, dance, and storytelling.
5. What role do parents play in developing emotional intelligence in children?
- Parents can model empathy, teach emotional regulation skills, and create a nurturing and supportive environment where emotions are acknowledged and validated.

A
You must be logged in to post a comment.